CRUD(Select)
The following uses the test-vona module as an example to explain the usage of Select in CRUD
Basic Query
The test-vona module defines the Post model. You can query Post data as follows
1. select
class ServicePost {
async select() {
return await this.scope.model.post.select();
}
}2. count
class ServicePost {
async count() {
return await this.scope.model.post.count();
}
}3. select and count
class ServicePost {
async selectAndCount() {
return await this.scope.model.post.selectAndCount();
}
}4. get
class ServicePost {
async get(id: TableIdentity) {
return await this.scope.model.post.get({ id });
}
}5. mget
class ServicePost {
async mget(ids: TableIdentity[]) {
return await this.scope.model.post.mget(ids);
}
}Select Type Definition
async select<
T extends IModelSelectParams<TRecord>,
ModelJoins extends TypeModelsClassLikeGeneral | undefined,
>(
params?: T,
options?: IModelMethodOptions,
_modelJoins?: ModelJoins,
): Promise<TRecord[]>;- Example: A relatively complex select query:
class ServicePost {
async select() {
return await this.scope.model.post.select({
columns: ['id', 'title', 'userId'],
where: {
'id': { _gt_: 1 },
'testVonaUser.id': 1,
},
joins: [['innerJoin', 'testVonaUser', ['userId', 'testVonaUser.id']]],
offset: 0,
limit: 20,
orders: [['createdAt', 'desc']],
}, {
disableDeleted: false,
}, 'test-vona:user');
}
}Select Parameter: Options
| Name | Type | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| disableDeleted | boolean | false | Disable soft deletion |
| disableCreateTime | boolean | false | Disable automatic creation time setting |
| disableUpdateTime | boolean | false | Disable automatic update time setting |
| disableCacheQuery | boolean | false | Disable Cache Query |
| disableCacheEntity | boolean | false | Disable Cache Entity |
| deleted | boolean | undefined | Can explicitly set the deleted value |
Select Parameter: Params
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| distinct | Whether to enable distinct |
| columns | List of fields to be queried |
| where | Conditional statement |
| joins | Related tables |
| orders | Sorting |
| limit | Can be used for paginated queries |
| offset | Can be used for paginated queries |
| include | Static relationships |
| with | Dynamic relationships |
orders
This is an array type, and multiple orders can be specified:
async select() {
return await this.scope.model.post.select({
orders: [
['createdAt', 'desc'],
['title', 'asc'],
],
});
}joins
You can use joins to join multiple tables
async select() {
return await this.scope.model.post.select({
joins: [
['innerJoin', 'testVonaUser', ['userId', 'testVonaUser.id']],
['leftJoin', 'testVonaPostContent', ['id', 'testVonaPostContent.postId']],
],
});
}joins supports type hinting, as shown in the figure:
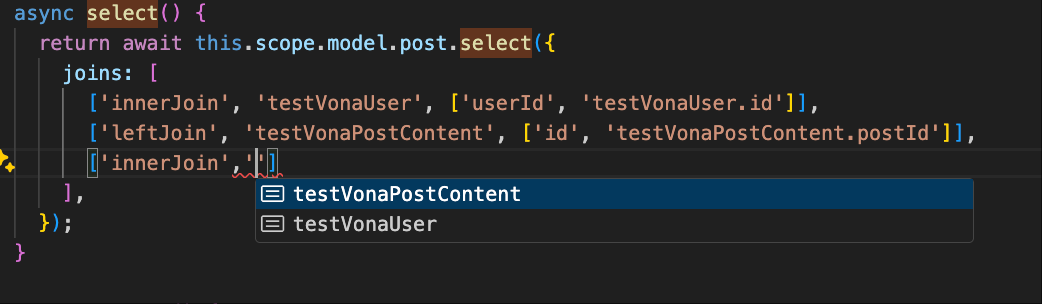
So, where does the list of tables shown in the figure come from?
As mentioned earlier, you can define relationships between multiple entities in a Model. Therefore, the system automatically extracts the corresponding data tables from the relationships defined in the model. The relationships for the Post model are defined as follows:
@Model({
relations: {
postContent: $relation.hasOne('test-vona:postContent', 'postId', { columns: ['id', 'content'] }),
user: $relation.belongsTo(() => ModelPost, () => ModelUser, 'userId', { autoload: true, columns: ['id', 'name'] }),
},
})
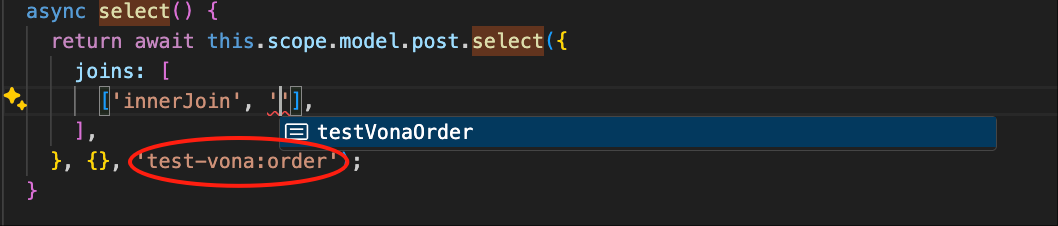
class ModelPost {}In a large business system, a model may not define all relationships. Alternatively, you can specify the models to be associated using the _modelJoins parameter, and the system will retrieve the corresponding data tables from these models
For example, the test-vona module defines the order model. Then, we can use joins like this:
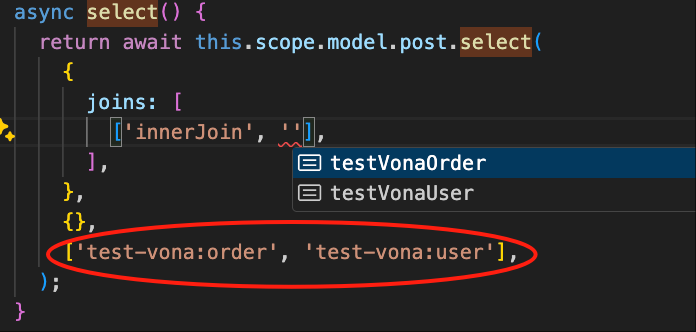
We can also specify multiple models:
where: Normal Operators
1. Basic usage
class ServicePost {
async select() {
return await this.scope.model.post.select({
where: {
title: { _includes_: 'ai' },
stars: { _gt_: 20 },
},
});
}
}class ServicePost {
async select() {
return await this.scope.model.post.select({
where: {
stars: {
_gt_: 20,
_lt_: 50,
},
},
});
}
}2. List of Normal Operators
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| _eq_ | |
| _notEq_ | |
| _gt_ | |
| _gte_ | |
| _lt_ | |
| _lte_ | |
| _in_ | |
| _notIn_ | |
| _is_ | value值为null或undefined |
| _isNot_ | value值为null或undefined |
| _between_ | |
| _notBetween_ | |
| _startsWith_ | |
| _endsWith_ | |
| _includes_ | |
| _startsWithI_ | Insensitive string operator |
| _endsWithI_ | Insensitive string operator |
| _includesI_ | Insensitive string operator |
| _ref_ | value is an identifier |
| _skip_ | If value is equal to _skip, ignore the current contition |
3. Examples
- Array
class ServicePost {
async select() {
return await this.scope.model.post.select({
where: {
title: {
_in_: ['ai', 'web'],
},
},
});
}
}select * from "testVonaPost" where ("title" in ('ai', 'web'))
class ServicePost {
async select() {
return await this.scope.model.post.select({
where: {
title: ['ai', 'web'],
},
});
}
}select * from "testVonaPost" where "title" in ('ai', 'web')
- Check if empty
class ServicePost {
async select() {
return await this.scope.model.post.select({
where: {
title: {
_is_: null,
},
},
});
}
}select * from "testVonaPost" where ("title" is null)
class ServicePost {
async select() {
return await this.scope.model.post.select({
where: {
title: null,
},
});
}
}select * from "testVonaPost" where "title" is null
- _ref_
class ServicePost {
async select() {
return await this.scope.model.post.select({
where: {
title: {
_ref_: 'title',
},
},
});
}
}select * from "testVonaPost" where ("title" = "title")
class ServicePost {
async select() {
return await this.scope.model.post.select({
where: {
title: {
_ref_: 'testVonaPost.title',
},
},
});
}
}select * from "testVonaPost" where ("title" = "testVonaPost"."title")
- _skip_
class ServicePost {
async select() {
const where = {
title: { _includes_: 'ai' },
stars: { _gt_: 20 },
};
return await this.scope.model.post.select({
where: {
...where,
stars: '_skip_' as const,
},
});
}
}select * from "testVonaPost" where ("title" like '%ai%')
where: Joint Operators
1. Basic Usage
class ServicePost {
async select() {
return await this.scope.model.post.select({
where: {
_or_: {
title: { _includes_: 'ai' },
stars: { _gt_: 20 },
},
},
});
}
}select * from "testVonaPost" where ((("title" like '%ai%')) or (("stars" > 20)))
class ServicePost {
async select() {
return await this.scope.model.post.select({
where: {
stars: {
_or_: {
_lt_: 20,
_gt_: 50,
},
},
},
});
}
}select * from "testVonaPost" where ((("stars" < 20) or ("stars" > 50)))
2. List of Joint Operators
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| _and_ | |
| _or_ | |
| _not_ | |
| _exists_ | |
| _notExists_ |
3. Examples
- _not_
class ServicePost {
async select() {
return await this.scope.model.post.select({
where: {
_not_: {
title: { _includes_: 'ai' },
stars: { _gt_: 20 },
},
},
});
}
}select * from "testVonaPost" where not (("title" like '%ai%') and ("stars" > 20))
- _exists_
class ServicePost {
async select() {
return await this.scope.model.post.select({
where: {
_exists_: function (builder: Knex.QueryBuilder) {
builder
.select('*')
.from('testVonaPostContent')
.where('postId', this.scope.model.post.ref('testVonaPost.id'));
} as any,
},
});
}
}select * from "testVonaPost" where exists (select * from "testVonaPostContent" where "postId" = "testVonaPost"."id")
where:raw
class ServicePost {
async select() {
return await this.scope.model.post.select({
where: this.scope.model.post.raw('?? > ?', ['stars', 20]) as any,
});
}
}select * from "testVonaPost" where "stars" > 20
where:ref
class ServicePost {
async select() {
return await this.scope.model.post.select({
where: {
title: {
'_eq_': this.scope.model.post.ref('title') as any,
}
},
});
}
}select * from "testVonaPost" where ("title" = "title")
class ServicePost {
async select() {
return await this.scope.model.post.select({
where: {
title: {
'_eq_': this.scope.model.post.ref('testVonaPost.title') as any,
}
},
});
}
}select * from "testVonaPost" where ("title" = "testVonaPost"."title")