External Aspect
Applies logic to any method of any class from the outside without changing the class source code
Create Target Class
External aspect can be implemented for any class. Below, taking Service as an example, create a Service test in the module demo-student with the following code:
@Service()
export class ServiceTest extends BeanBase {
private _name: string;
protected __init__() {
this._name = '';
}
protected async __dispose__() {
this._name = '';
}
get name() {
return this._name;
}
set name(value) {
this._name = value;
}
actionSync(a: number, b: number) {
return a + b;
}
async actionAsync(a: number, b: number) {
return Promise.resolve(a + b);
}
}Create External Aspect
Next, create an external aspect log to provide extension logic for the properties and methods of Class ServiceTest
1. Cli command
$ vona :create:bean aop log --module=demo-student2. Menu command
TIP
Context Menu - [Module Path]: Vona Aspect/Aop
AOP Definition
import { BeanAopBase } from 'vona';
import { Aop } from 'vona-module-a-aspect';
@Aop({ match: 'demo-student.service.test' })
export class AopLog extends BeanAopBase {}@Aop: This decorator is used to implement theexternal aspectmatch: This option is used to associate theAopLogclass with theServiceTestclass, which beanFullName isdemo-student.service.test
| name | type | description |
|---|---|---|
| match | string|regexp|(string|regexp)[] | For which classes to enable |
Aspect: Synchronous method
Outputs execution time for ServiceTest#actionSync
In the VSCode editor, enter the code snippet aopactionsync to automatically generate a code skeleton:
action: AopAction<ClassSome, 'action'> = (_args, next, _receiver) => {
return next();
};Adjust the code and add log logic
actionSync: AopAction<ServiceTest, 'actionSync'> = (_args, next, _receiver) => {
const timeBegin = Date.now();
const res = next();
const timeEnd = Date.now();
console.log('actionSync: ', timeEnd - timeBegin);
return res;
};actionSync: Provides theactionSyncmethod with the same name to implement custom logic
Aspect: Asynchronous method
Outputs execution time for ServiceTest#actionAsync
In the VSCode editor, enter the code snippet aopaction to automatically generate a code skeleton:
action: AopAction<ClassSome, 'action'> = async (_args, next, _receiver) => {
return await next();
};Adjust the code and add log logic
actionAsync: AopAction<ServiceTest, 'actionAsync'> = async (_args, next, _receiver) => {
const timeBegin = Date.now();
const res = await next();
const timeEnd = Date.now();
console.log('actionAsync: ', timeEnd - timeBegin);
return res;
};actionAsync: Provides theactionAsyncmethod with the same name to implement custom logic
Aspect: getter
Outputs execution time for ServiceTest#get name
In the VSCode editor, enter the code snippet aopgetter to automatically generate a code skeleton:
protected __get_xxx__: AopActionGetter<ClassSome, 'xxx'> = function (next, _receiver) {
const value = next();
return value;
};Adjust the code and add log logic
protected __get_name__: AopActionGetter<ServiceTest, 'name'> = function (next, _receiver) {
const timeBegin = Date.now();
const value = next();
const timeEnd = Date.now();
console.log('get name: ', timeEnd - timeBegin);
return value;
};__get_name__: Corresponding to the getter methodget nameofServiceTest
Aspect: setter
Outputs execution time for ServiceTest#set name
In the VSCode editor, enter the code snippet aopsetter to automatically generate a code skeleton:
protected __set_xxx__: AopActionSetter<ClassSome, 'xxx'> = function (value, next, _receiver) {
return next(value);
}Adjust the code and add log logic
protected __set_name__: AopActionSetter<ServiceTest, 'name'> = function (value, next, _receiver) {
const timeBegin = Date.now();
const res = next(value);
const timeEnd = Date.now();
console.log('set name: ', timeEnd - timeBegin);
return res;
};__set_name__: Corresponding to the setter methodset nameofServiceTest
Aspect: __init__
Outputs execution time for ServiceTest#__init__
In the VSCode editor, enter the code snippet aopinit to automatically generate a code skeleton:
protected __init__: AopActionInit<ClassSome> = (_args, next, _receiver) => {
next();
};Adjust the code and add log logic
protected __init__: AopActionInit<ServiceTest> = (_args, next, _receiver) => {
const timeBegin = Date.now();
next();
const timeEnd = Date.now();
console.log('__init__: ', timeEnd - timeBegin);
};__init__: Provides the__init__method with the same name to implement custom logic
Aspect: __dispose__
Outputs execution time for ServiceTest#__dispose__
In the VSCode editor, enter the code snippet aopdispose to automatically generate a code skeleton:
protected __dispose__: AopActionDispose<ClassSome> = async (_args, next, _receiver) => {
await next();
};Adjust the code and add log logic
protected __dispose__: AopActionDispose<ServiceTest> = async (_args, next, _receiver) => {
const timeBegin = Date.now();
await next();
const timeEnd = Date.now();
console.log('__dispose__: ', timeEnd - timeBegin);
};__dispose__: Provides the__dispose__method with the same name to implement custom logic
Aspect: __get__
Extending magic method for ServiceTest
- See: Magic Method
In the VSCode editor, enter the code snippet aopget to automatically generate a code skeleton:
protected __get__: AopActionGet<ClassSome> = (_prop, next, _receiver) => {
const value = next();
return value;
};Adjust the code and add the custom field red
protected __get__: AopActionGet<ServiceTest> = (prop, next, _receiver) => {
if (prop === 'red') return '#FF0000';
const value = next();
return value;
};__get__: Conventional magic method name
Provide type definitions for colors using the interface type merging mechanism
declare module 'vona-module-demo-student' {
export interface ServiceTest {
red: string;
}
}Aspect: __set__
Extending magic method for ServiceTest
- See: Magic Method
In the VSCode editor, enter the code snippet aopset to automatically generate a code skeleton:
protected __set__: AopActionSet<ClassSome> = (_prop, value, next, _receiver) => {
return next(value);
};Adjust the code to set the value for the custom field red
private _colorRed: string | undefined;
protected __set__: AopActionSet<ServiceTest> = (prop, value, next, _receiver) => {
if (prop === 'red') {
this._colorRed = value;
return true;
}
return next(value);
};__set__: Conventional magic method name- If a value is set for
prop, returntrue; otherwise, invokenextmethod
Then adjust the __get__ logic:
protected __get__: AopActionGet<ServiceTest> = (prop, next, _receiver) => {
- if (prop === 'red') return '#FF0000';
+ if (prop === 'red') return this._colorRed;
const value = next();
return value;
}Aspect: __method__
Extending logic for any method of ServiceTest
In the VSCode editor, enter the code snippet aopmethod to automatically generate a code skeleton:
protected __method__: AopActionMethod<ClassSome> = (_method, _args, next, _receiver) => {
return next();
};Adjust the code and add log logic for actionSync and actionAsync
protected __method__: AopActionMethod<ServiceTest> = (method, _args, next, _receiver) => {
if (method !== 'actionSync' && method !== 'actionAsync') {
return next();
}
const timeBegin = Date.now();
function done(res) {
const timeEnd = Date.now();
console.log(`method ${method}: `, timeEnd - timeBegin);
return res;
}
const res = next();
if (res?.then) {
return res.then((res: any) => {
return done(res);
});
}
return done(res);
};__method__: Conventional magic method nameres?.then: Determine whether the return value is a Promise object and perform different processing to make it compatible withsynchronous methodandasynchronous method
AOP Order
For the same target Class, multiple AOPs can be associated. Therefore, VonaJS provides two parameters to control the execution order of AOPs
1. dependencies
For example, has another AOP demo-student:log3, and we hope that the execution order is as follows: demo-student:log3 > Current
@Aop({
match: 'demo-student.service.test',
+ dependencies: 'demo-student:log3',
})
class AopLog {}2. dependents
The order of dependents is just the opposite of dependencies. We hope that the execution order is as follows: Current > demo-student:log3
@Aop({
match: 'demo-student.service.test',
+ dependents: 'demo-student:log3',
})
class AopLog {}AOP Enable/Disable
You can control enable/disable of AOPs
1. Enable
src/backend/config/config/config.ts
// onions
config.onions = {
aop: {
'demo-student:log': {
+ enable: false,
},
},
};2. Meta
Allows AOPs to take effect in a specified operating environment
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| flavor | string|string[] | See: Runtime Environments and Flavors |
| mode | string|string[] | See: Runtime Environments and Flavors |
- Example
@Aop({
+ meta: {
+ flavor: 'normal',
+ mode: 'dev',
+ },
})
class AopLog {}Inspect
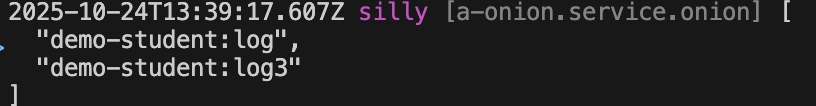
You can directly inspect the currently effective AOP list in the target class action
class ServiceTest {
protected async __dispose__() {
+ this.bean.onion.aop.inspect();
this._name = '';
}this.bean.onion: Get the global Service instanceonion.aop: Get the Service instance related to AOP.inspect: Output the currently effective AOP list
When the method is executed, the currently effective AOP list will be automatically output to the console, as shown below: