Migration and Changes
Vona provides a unique migration mechanism that adapts to the development and continuous iteration of large projects
Features
Support modular system: Take business modules as units, automatically detect whether the module has changed when the system starts, and automatically execute the change logicSupport multi-tenancy: Provide independent initialization data for different tenantsSupport unit-test: Provide test data for the test environmentSupport production environment: Can be executed safely and effectively in the production environmentSupport type system: Provide type hints to make the code higher quality and easier to maintainMore powerful execution environment: Migration code can use the complete ecosystem provided by Vona
Define data version
Configure the current data version of the module in the module's package.json
src/module/demo-student/package.json
{
"name": "vona-module-demo-student",
"vonaModule": {
"fileVersion": 1
},
}- fileVersion: When the module has been released, the next time the database schema changes,
fileVersionneeds to be incremented by+1
Create meta.version
Vona uses Bean meta.version to uniformly manage module migration codes
1. Cli command
$ vona :create:bean meta version --module=demo-student2. Menu command
TIP
Context Menu - [Module Path]: Vona Meta/Version
meta.version Definition
@Meta()
export class MetaVersion extends BeanBase {}Change-scenario
Vona provides three change-scenarios. You can inherit the corresponding interface and implement the corresponding method according to business needs
| Scenario | Interface | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| update | IMetaVersionUpdate | update | Changes in database schema, such as creating a new data table, adding fields, etc. |
| init | IMetaVersionInit | init | Provide initialization data for different instances/tenants |
| test | IMetaVersionTest | test | Provide test data for the test environment |
update: Database schema migration
For example, the current data version of the module demo-student is 1, and we create a data table demoStudent for version 1
@Meta()
export class MetaVersion extends BeanBase implements IMetaVersionUpdate {
async update(options: IMetaVersionUpdateOptions) {
if (options.version === 1) {
await this.bean.model.createTable('demoStudent', table => {
table.basicFields();
table.string('name', 50);
table.string('description', 255);
});
}
}
}table.basicFields: Create 5 basic fields:id/iid/deleted/createdAt/updatedAttable.string: Create a field of typestring
Vona uses knex at the bottom. For more details, see: knex
In order to make the code higher quality and easier to maintain, we can also use a typed code style
@Meta()
export class MetaVersion extends BeanBase implements IMetaVersionUpdate {
async update(options: IMetaVersionUpdateOptions) {
if (options.version === 1) {
const entityStudent = this.scope.entity.student;
await this.bean.model.createTable(entityStudent.$table, table => {
table.basicFields();
table.string(entityStudent.name, 50);
table.string(entityStudent.description, 255);
});
}
}
}init: Initialize data
For example, we initialize a student data
@Meta()
export class MetaVersion extends BeanBase implements IMetaVersionInit {
async init(options: IMetaVersionInitOptions) {
if (options.version === 1) {
await this.scope.model.student.insert({
name: 'Tom',
description: 'This is a student',
});
}
}
}Automatically write data in the database:
{
id: '1',
createdAt: 2025-07-03T13:39:22.642Z,
updatedAt: 2025-07-03T13:39:22.642Z,
deleted: false,
iid: 1,
name: 'Tom',
description: 'This is a student'
}Where iid: 1 is the Id of the current instance/tenant. Therefore, if there are multiple instances/tenants, the init method will be executed once for each instance/tenant. Therefore, the data of instances/tenants are isolated
test: test data
For example, add a student data, which is only used in the test environment
@Meta()
export class MetaVersion extends BeanBase implements IMetaVersionTest {
async test(_options: IMetaVersionTestOptions) {
await this.scope.model.student.insert({
name: 'Jimmy',
description: 'Only used in unit test',
});
}
}- The data added in the
testmethod is only valid in the test/development environment, and thetestmethod will not be executed in the production environment
Version change
If we need to create a new data table, such as Book, in subsequent business iterations. Then, the execution steps are as follows:
1. Increment fileVersion
{
"name": "vona-module-demo-student",
"vonaModule": {
- "fileVersion": 1
+ "fileVersion": 2
},
}2. Create Entity: EntityBook
@Entity('demoStudentBook')
export class EntityBook {
@Api.field()
name: string;
}3. Modify update/init/test
Write migration code in update/init/test as needed. Here, we only need to create a new data table in update
@Meta()
export class MetaVersion extends BeanBase implements IMetaVersionUpdate {
async update(options: IMetaVersionUpdateOptions) {
if (options.version === 1) {
...
}
if (options.version === 2) {
const entityBook = this.scope.entity.book;
await this.bean.model.createTable(entityBook.$table, table => {
table.basicFields();
table.string(entityBook.name, 255);
});
}
}
}4. Execute migration code
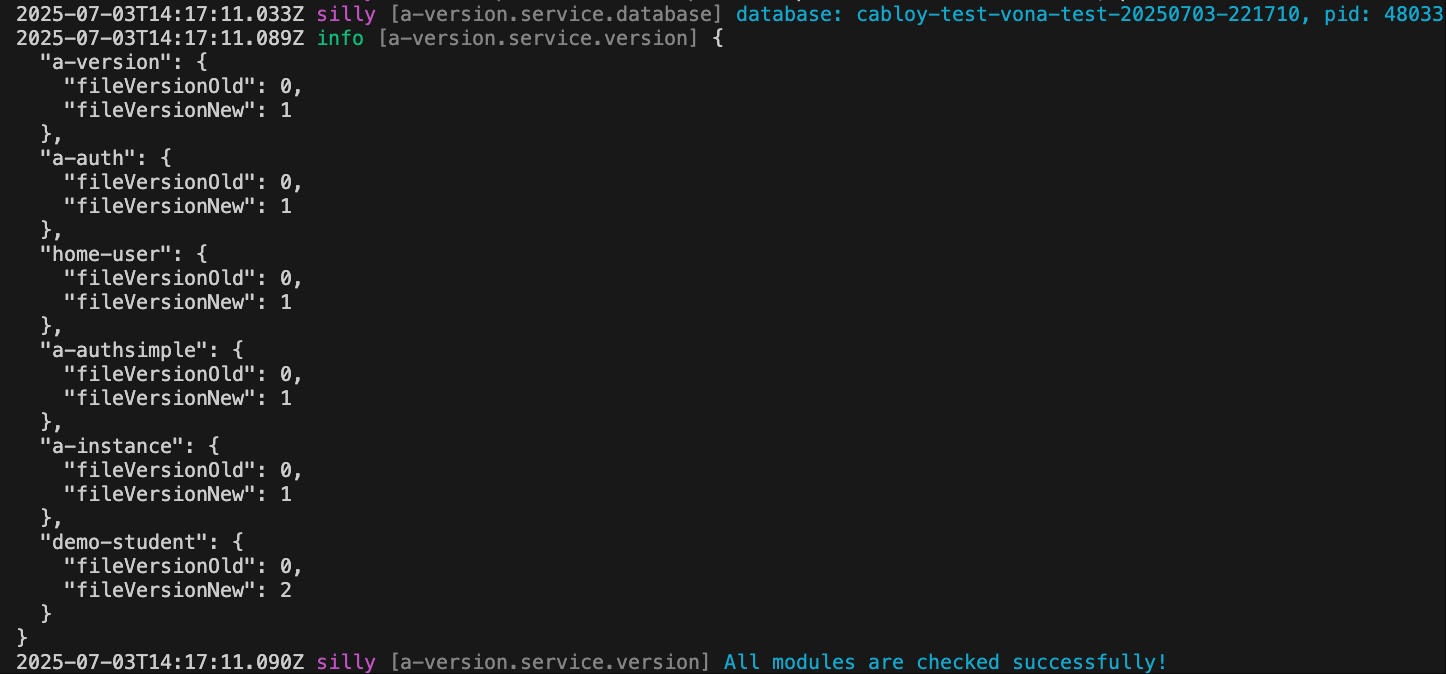
When the system starts, it will automatically detect whether the module needs to be changed, and automatically execute the migration code
# Development environment
$ npm run dev
# Production environment
$ npm run start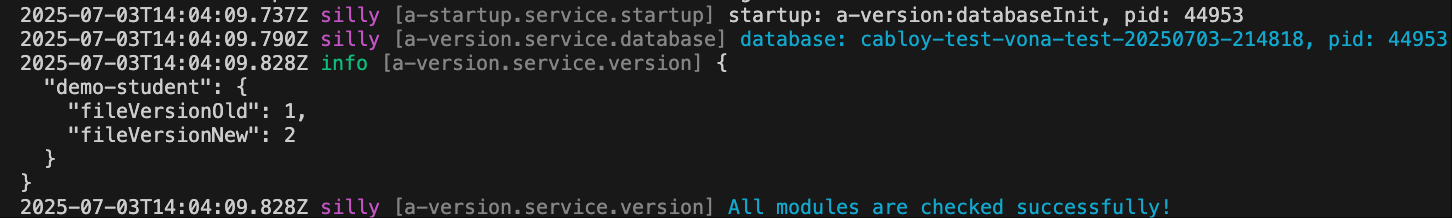
Support local development
When we develop locally, we need to frequently update the database schema for the current data version. Then, we do not need to modify fileVersion, but execute the following command to make the migration code effective
$ npm run testWhen we run this command, the system will automatically delete the old database and create a new database, which will re-execute the migration code and then execute unit tests
$ npm run db:resetThis command is only used to recreate the database and re-execute the migration code; it does not execute unit tests