Global Guard
Create Guard
For example, create a global guard admin in the module demo-student to check whether the current username is admin. If not, an exception is thrown
1. Cli command
$ vona :create:bean guard admin --module=demo-student --boilerplate=global2. Menu command
TIP
Context Menu - [Module Path]: Vona Aspect/Guard Global
Guard Definition
export interface IGuardOptionsAdmin extends IDecoratorGuardOptionsGlobal {}
@Guard<IGuardOptionsAdmin>()
@Global()
export class GuardAdmin {
async execute(_options: IGuardOptionsAdmin, next: Next): Promise<boolean> {
const user = this.ctx.user;
if (!user || user.name !== 'admin') this.app.throw(403);
// next
return next();
}
}getCurrentUser: Get the current user
Using Guard
Unlike local guard, the system automatically loads global guards and makes them effective
Guard Parameters
You can define parameters for guard, allowing for more flexible configuration of guard logic
For example, define the name parameter for the admin guard to control the username that needs to be judged
1. Defining parameter types
export interface IGuardOptionsAdmin extends IDecoratorGuardOptionsGlobal {
+ name: string;
}2. Providing default values for parameters
@Guard<IGuardOptionsAdmin>({
+ name: 'admin',
})3. Using Parameters
export interface IGuardOptionsAdmin extends IDecoratorGuardOptionsGlobal {
name: string;
}
@Guard<IGuardOptionsAdmin>({
name: 'admin',
})
export class GuardAdmin extends BeanBase implements IGuardExecute {
async execute(options: IGuardOptionsAdmin, next: Next): Promise<boolean> {
const user = this.ctx.user;
- if (!user || user.name !== 'admin') this.app.throw(403);
+ if (!user || user.name !== options.name) this.app.throw(403);
// next
return next();
}
}4. Specify parameters when using
You can specify global guard parameters for a specific API
class ControllerStudent {
@Web.get()
+ @Aspect.guardGlobal('demo-student:admin', { name: 'other-name' })
async findMany() {}
}- When using guard, just provide the parameter value directly
5. App Config
Guard parameters can be configured in App Config
src/backend/config/config/config.ts
// onions
config.onions = {
guard: {
'demo-student:admin': {
name: 'other-name',
},
},
};6. Parameter precedence
Specify parameters when using > App Config > Default values
Guard Order
Since global guards ard loaded and enabled by default, VonaJS provides two parameters to control the order in which guard is loaded
1. dependencies
For example, the system has a built-in global guard a-user:passport, and we hope that the loading order is as follows: a-user:passport > Current
@Guard({
+ dependencies: 'a-user:passport',
name: 'admin',
})
class GuardAdmin {}2. dependents
The order of dependents is just the opposite of dependencies. We hope that the loading order is as follows: Current > a-user:passport
@Guard({
+ dependents: 'a-user:passport',
name: 'admin',
})
class GuardAdmin {}Guard Enable/Disable
You can control enable/disable of global guard for certain APIs
1. Enable
- Disable for an API
class ControllerStudent {
@Web.get()
+ @Aspect.guardGlobal('demo-student:admin', { enable: false })
async findMany() {}
}- Disable for all APIs
src/backend/config/config/config.ts
// onions
config.onions = {
guard: {
'demo-student:admin': {
+ enable: false,
},
},
};2. Meta
Allows global guard to take effect in a specified operating environment
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| flavor | string|string[] | See: Runtime Environments and Flavors |
| mode | string|string[] | See: Runtime Environments and Flavors |
- Example
@Guard({
+ meta: {
+ flavor: 'normal',
+ mode: 'dev',
+ },
})
class GuardAdmin {}3. match/ignore
You can enable/disable global guard for some specific APIs
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| match | string|regexp|(string|regexp)[] | For which APIs to enable |
| ignore | string|regexp|(string|regexp)[] | For which APIs to disable |
Inspect
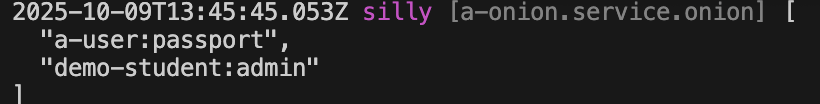
You can directly inspect the currently effective global guard list in the Controller action
class ControllerStudent {
@Web.get()
async findMany() {
+ this.bean.onion.guard.inspect();
}
}this.bean.onion: Get the global Service instanceonion.guard: Get the Service instance related to the guard.inspect: Output the currently effective global guard list
When accessing the findMany API, the current list of global guard in effect will be automatically output to the console, as shown below: