Entity
Create Entity
For example, we create an Entity student in the module demo-student
1. Cli command
$ vona :create:bean entity student --module=demo-student2. Menu command
TIP
Context Menu - [Module Path]: Vona Create/Entity
Entity Definition
+ @Entity<IEntityOptionsStudent>('demoStudent')
export class EntityStudent extends EntityBase {}- Set the corresponding data table name
table name
Vona is a modular system, and different modules can manage their own data tables independently. In order to avoid table name conflicts, Vona has agreed on a default combination mechanism for data table names. Of course, you can also provide your own table name, but you need to evaluate the risk of table name conflicts yourself
1. General format
tableName = moduleName + entityNameFor example, the entity book of the module demo-student has a corresponding data table name of: demoStudentBook
2. Simplified rules
If entityName has the same name as moduleName, the duplicate part will be automatically removed
For example, the entity student of the module demo-student has a corresponding data table name of: demoStudent
@Api.field
Generally speaking, when defining a field, you need to specify the field type, validation rules, and Swagger/Openapi metadata
In Entity You only need to use the @Api.field decorator to provide all the above information, making the code more concise and intuitive
The parameter usage mechanism of the @Api.field decorator is similar to the Controller request parameter, see:
Field type and validation rules
1. Automatically infer Zod Schema: Basic type/Dto/Entity
If the field type is Basic type/Dto/Entity, then the system will automatically infer the corresponding Zod Schema and automatically generate Swagger/Openapi
- Example:
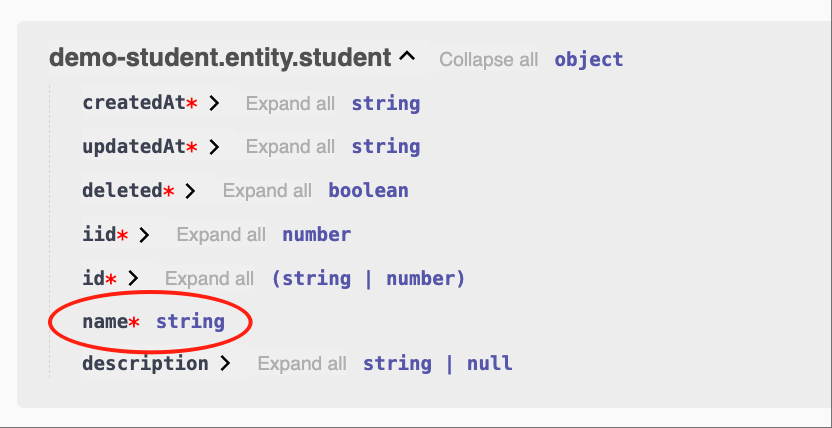
string
class EntityStudent {
@Api.field()
name: string;
}
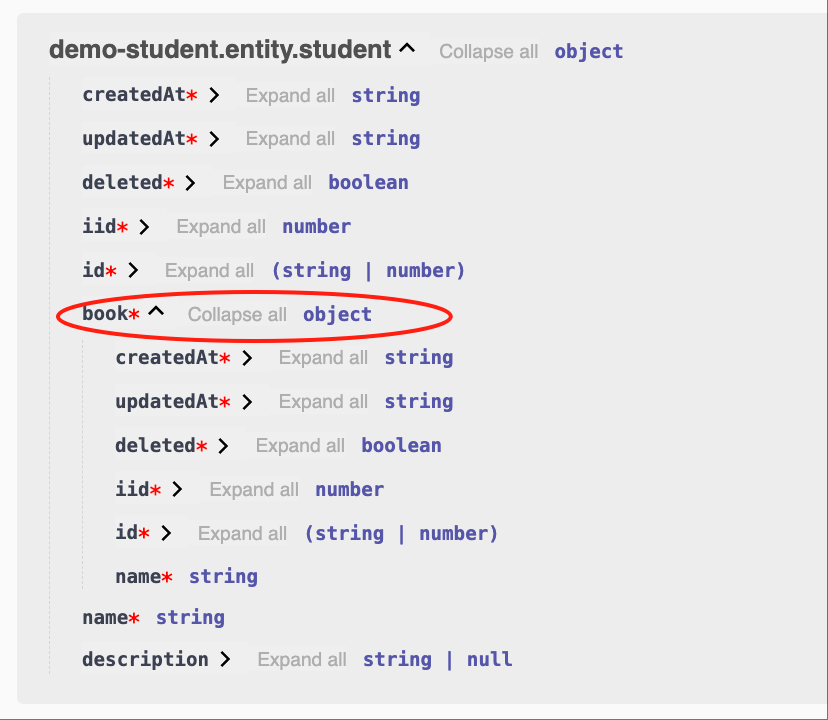
- Example:
EntityBook
class EntityStudent {
@Api.field()
book: EntityBook;
}
- List of automatically inferred types
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| string | z.string() |
| number | z.number() |
| boolean | z.boolean() |
| Dto | z.object({...}) |
| Entity | z.object({...}) |
2. Specify Zod Schema
We can also explicitly specify Zod Schema and automatically generate Swagger/Openapi
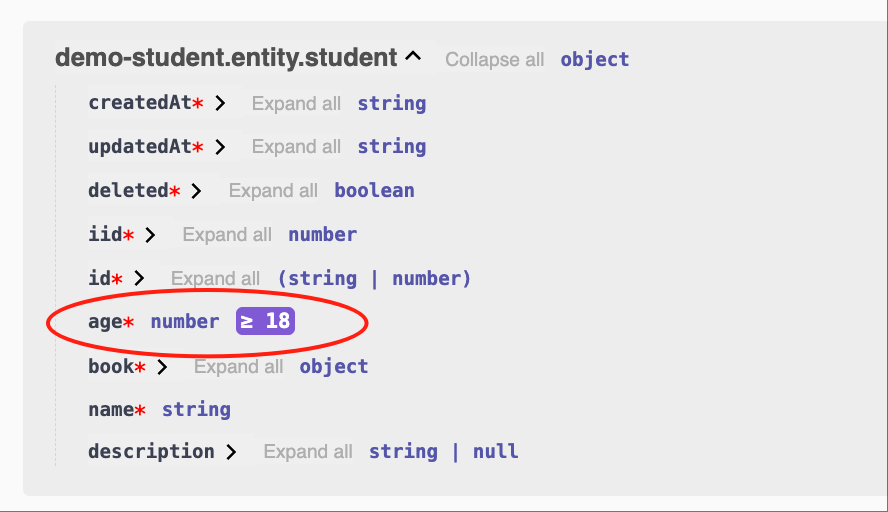
- Example:
number, >=18
class EntityStudent {
@Api.field(z.number().min(18))
age: number;
}
3. Extending Zod Schema properties
We can also extend new properties based on the existing Zod Schema
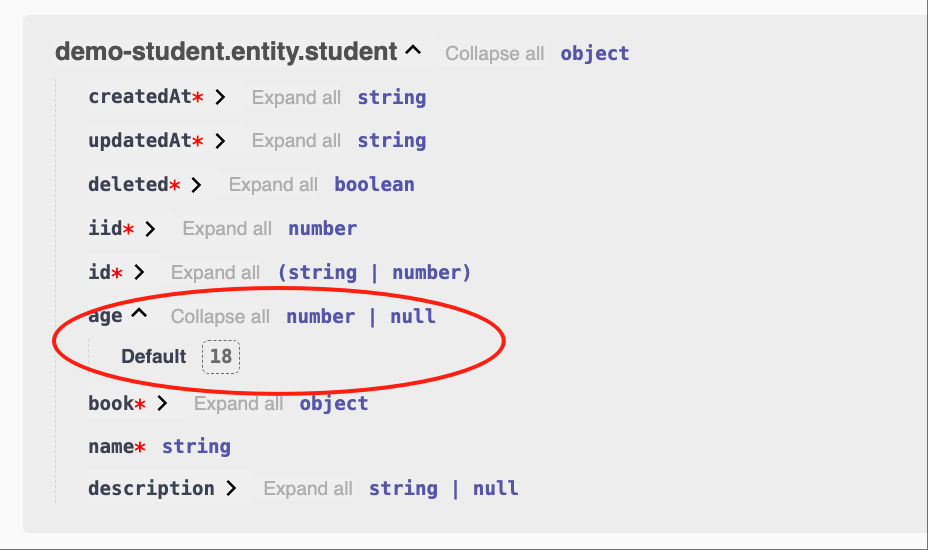
- Example:
number, optional, default value is 18
class EntityStudent {
@Api.field(v.default(18), v.optional())
age?: number;
}The above code is equivalent to:
class EntityStudent {
@Api.field(z.number().optional().default(18))
age?: number;
}Also equivalent to:
class EntityStudent {
@Api.field(v.default(18), z.number().optional())
age?: number;
}
4. Special tool: Array
For Array type parameters, Vona also provides convenient tools
- Example:
number[]
class EntityStudent {
@Api.field(v.array(Number))
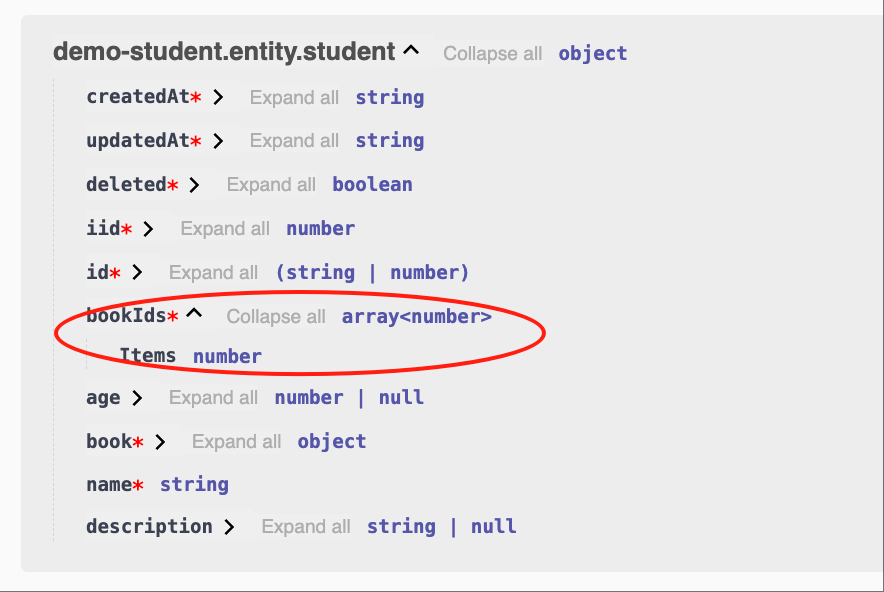
bookIds: number[];
}Equivalent to:
class EntityStudent {
@Api.field(v.array(z.number()))
bookIds: number[];
}
- Example:
EntityBook[]
class EntityStudent {
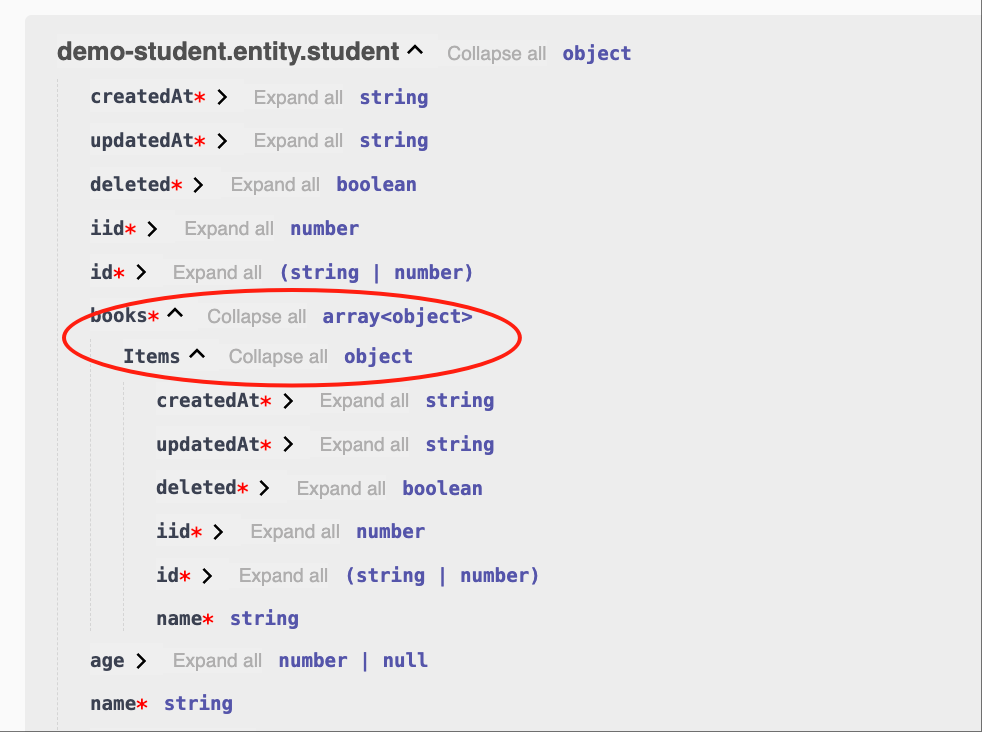
@Api.field(v.array(EntityBook))
books: EntityBook[];
}
These utility methods for extending Zod Schema are put into the decorator group v to reduce the mental burden
Swagger/Openapi
Vona also provides many extension tools for setting metadata related to Openapi
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| v.default | default |
| v.optional | optional |
| v.openapi | openapi |
| v.title | title |
| v.description | description |
| v.example | example |
1. Example: v.title
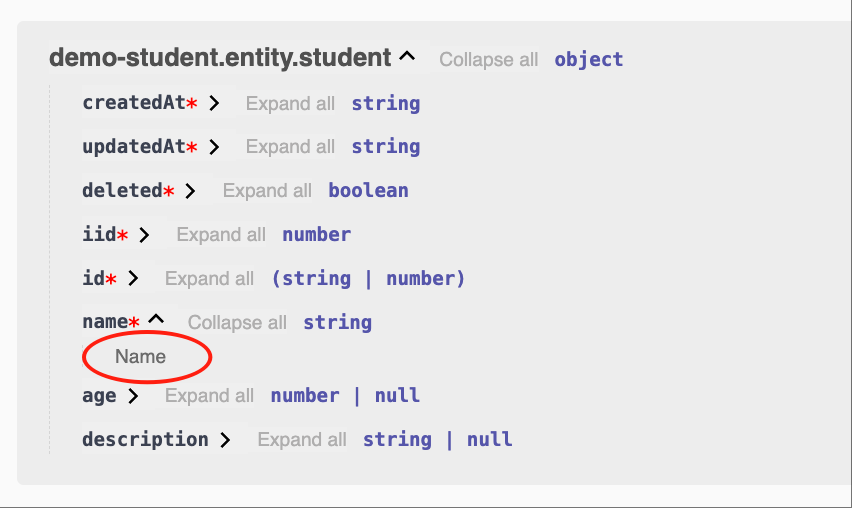
title='Name'
class EntityStudent {
@Api.field(v.title('Name'))
name: string;
}
2. Example: v.openapi
We can use v.openapi to set more metadata at once
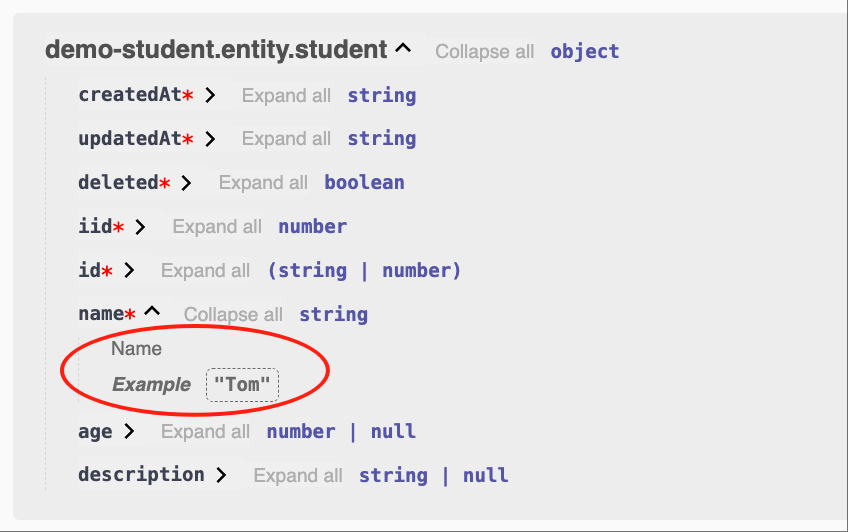
title='Name', example='Tom'
class EntityStudent {
@Api.field(v.openapi({ title: 'Name', example: 'Tom' }))
name: string;
}
I18n
Vona provides I18n for Openapi. For example, title is Name, and the steps to support multiple languages are as follows:
1. Provide language resources
For how to add language resources, see: I18n
- English:
src/module/demo-student/src/config/locale/en-us.ts
export default {
Name: 'Name',
};- Chinese:
src/module/demo-student/src/config/locale/zh-cn.ts
export default {
Name: '姓名',
};2. Use $locale
Use the $locale method for language translation, and support automatic type hints for language resources
import { $locale } from '../.metadata/locales.ts';
@Api.field(v.title($locale('Name')))- English
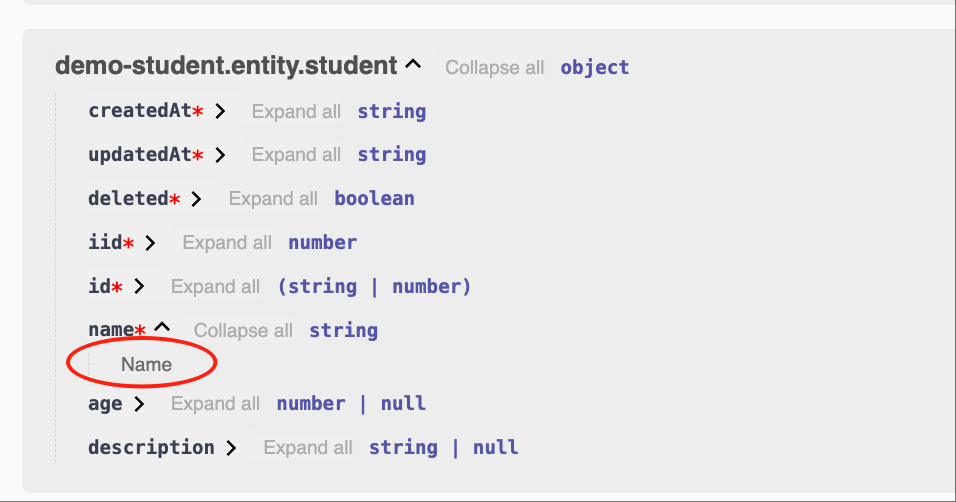
- Chinese
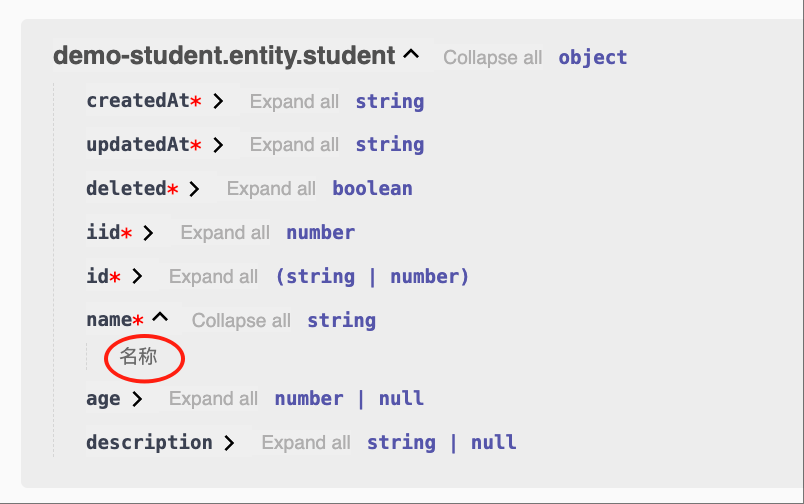
Entity Options
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| table | The table name corresponding to entity |
| independent | Whether to display independently in Swagger/Openapi, the default is false |
| openapi | Metadata related to Swagger/Openapi |
| fields | Define Fields options |
- independent: If the Controller Action references entity, then the entity will be automatically output to Swagger/Openapi. If
independent: trueis specified, the entity will always be output to Swagger/Openapi
1. Example: openapi
Provide description information for entity so that it can be displayed in Swagger/Openapi
@Entity({
openapi: { description: 'Student' },
})
class EntityStudent {}- Support I18n
English: src/module/demo-student/src/config/locale/en-us.ts
export default {
Student: 'Student',
};Chinese: src/module/demo-student/src/config/locale/zh-cn.ts
export default {
Student: '学生',
};import { $locale } from '../.metadata/locales.ts';
@Entity({
openapi: { description: $locale('Student') },
})
class EntityStudent {}2. Example: fields
Change the validation rules of the field age to: number, optional, default value is 16
Change the openapi metadata of the field name to: title: 'Student Name'
@Entity({
fields: {
age: z.number().optional().default(16),
name: { title: 'Student Name' },
},
})
class EntityStudent {}App Config
Entity options can be configured in App Config
src/backend/config/config/config.ts
// onions
config.onions = {
entity: {
'demo-student:student': {
openapi: {
description: 'Student',
},
fields: {
age: z.number().optional().default(16),
name: { title: 'Student Name' },
},
},
},
};Base class: EntityBase
By default, entity inherits from the base class EntityBase. EntityBase provides several commonly used fields. You can implement your own base class according to business needs
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | TableIdentity | TableIdentity is a union type of string and number |
| createdAt | Date | Creation time |
| updatedAt | Date | Update time |
| deleted | boolean | Soft deletion |
| iid | number | Instance ID/Tenant ID |
- id: Use the
TableIdentitytype to support business systems of any size
id: TableIdentity
The key field id uses the TableIdentity type to support business systems of any size. When we use int64 as the database field type, the value read from the database is of string type
export type TableIdentity = string | number;- Set the default field type
When creating a data table, the system will use number or bigint as the type of the id field according to the current configuration, and the default is bigint
src/backend/config/config/config.ts
// modules
config.modules = {
'a-orm': {
'table': {
identityType: 'bigint',
},
},
};