Startup
VonaJS provides startup, which allow initialization logic to be executed when system starting or when instance initializing
Startup Types
VonaJS provides two types of startups:
App Startup: Executed when system startingInstance Startup: Executed when instance initializing. Because VonaJS supportsMulti-Instance/Multi-Tenancy, theinstance startupsare automatically executed during each instance initialization
Create Startup
For example, create a startup log in the module demo-student to output the current time to the console when system starting
1. Cli Command
$ vona :create:bean startup log --module=demo-student2. Menu Command
TIP
Context menu - [Module Path]: Vona Bean/Startup
Startup Definition
@Startup()
export class StartupLog extends BeanBase implements IStartupExecute {
async execute() {
console.log('Current time: ', Date.now());
}
}execute: Outputs the current time
Startup Parameters
Parameters can be configured for startup
@Startup({
instance: false,
after: false,
debounce: true,
transaction: false,
})
export class StartupLog {}| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| instance | boolean | Whether it is an instance startup, defaults to false |
| after | boolean | Controls the timing of startup, defaults to false |
| debounce | boolean| number | Execute Startup using debounce, defaults to false |
| transaction | boolean | Whether to enable database transaction, defaults to false |
after:false: Executes beforeappReady(app startup) orinstanceReady(instance startup)true: Executes afterappReady(app startup) orinstanceReady(instance startup)
debouncefalse: Disable debouncetrue: Use the system's default debounce timenumber(ms): Specify the specific debounce time
App Config
You can configure startup parameters in App Config
src/backend/config/config/config.ts
// onions
config.onions = {
startup: {
'demo-student:log': {
after: false,
debounce: true,
instance: false,
transaction: false,
},
},
};Startup Order
Since startups ard loaded and enabled by default, VonaJS provides two parameters to control the order in which startup is loaded
1. dependencies
For example, the system has a built-in startup a-web:listen, and we hope that the loading order is as follows: a-web:listen > Current
@Startup({
+ dependencies: 'a-web:listen',
})
class StartupLog {}2. dependents
The order of dependents is just the opposite of dependencies. We hope that the loading order is as follows: Current > a-web:listen
@Startup({
+ dependents: 'a-web:listen',
})
class StartupLog {}Startup Enable/Disable
You can control enable/disable of startup
1. Enable
src/backend/config/config/config.ts
// onions
config.onions = {
startup: {
'demo-student:log': {
+ enable: false,
},
},
};2. Meta
Allows startup to take effect in a specified operating environment
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| flavor | string|string[] | See: Runtime Environments and Flavors |
| mode | string|string[] | See: Runtime Environments and Flavors |
- Example
@Startup({
+ meta: {
+ flavor: 'normal',
+ mode: 'dev',
+ },
})
class StartupLog {}Inspect
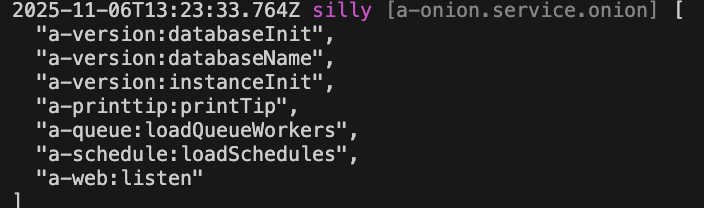
You can directly inspect the currently effective startup list
class ControllerStudent {
@Web.get('test')
test() {
+ this.bean.onion.startup.inspect();
}
}this.bean.onion: Get the global Service instanceonion.startup: Get the Service instance related to the startup.inspect: Output the currently effective startup list
When accessing the test API, the currently effective startup list will be automatically output to the console, as shown below: